DuBrute - a rare view into chinese blackhat techniques
As member of the MalwareMustDie ELF-Team, I was assigned to make report to dissect the DuBrute bruteforcing tool. This report is published on the effort as the first official report that hopefully can help good people in InfoSec.
We all know the ELF malware that comes from China. Linux/MrBlack, Linux/Xor.DDoS, Linux/BillGates are just a few of them. But what we don’t know is the way how our suspects are working. What is their common way to spread so much malware in only a few days? Which tools are they using? How do they work?
Our team has disclosed the video of the way how ELF malware can be spread via exploiting SSH in this malwaremustdie blog post:
http://blog.malwaremustdie.org/2014/11/china-elf-botnet-malware-infection.html
But new tools just come up to be used, this post explains one of the new used tools called “DUBrute”.
Due to the team’s research we have found a .zip archive in one of the chinese HFS panels. In this .zip archive we have found a picture and a directory called “DUBrute”.
Let us have a look on this directory:
14b2374efbd0d6ec435eb10d053db1c3 1.bat
8f4ec24aeda03afaae1cac0d7030dcf2 2.bat
abf1f45b4fa467b830f091cf96d82586 QtCore4.dll
21e38b4a1f28bdef99d1c7dac5dce164 QtGui4.dll
f971323ecd66fdd66468c6551c8eaa79 config.ini
bac0e8e8fa5d330bc0a58e440eab5812 dubrute.exe
cdbdef73515997355e81a99421c1d721 libeay32.dll
86f1895ae8c5e8b17d99ece768a70732 msvcr71.dll
6c06fb9e1d818fde8d142ee180a65646 ssleay32.dll
16f9d4cbd70328c0370d6587b8e48c05 xf.TXT
956958b308193d9f064d49f13a4d1ee1 xiaofe.dllSo what do we have? We have several different .dll (dynamic linked libraries) one .exe (Windows Executable), 2 batch files and one simple text file. So let us check out the dubrute.exe first:
dubrute.exe: PE32 executable (GUI) Intel 80386, for MS Windows
Filesize: 286720
MD5: bac0e8e8fa5d330bc0a58e440eab5812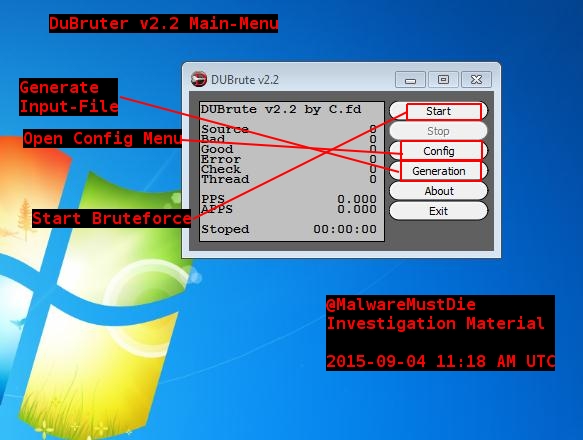
This is the main-menu of the DuBrute v2.2. It is pretty simple. “Start” starts the bruteforce and “Stop” stops it. “Config” opens the config-menu, “Generation” generates an input file for the tool and “Exit” exits the programm. The input file is called “Source”. All successful logins will go into a file called “good.txt”, errors will go into “error.txt” and IP’s without a result will go into “bad.txt”. Let us see the dubrute config menu:
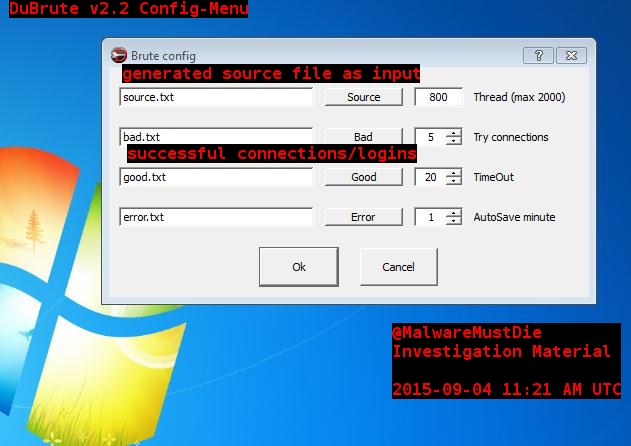
Additional to the filepaths for the output files you can set different other options like “Thread rate”, “Connections”, “TimeOut” and “AutoSave”.
The next picture is more interesting. This is the source.txt-Generator. With this tool they can create an input file. This input file contains the IP’s, logins and passwords.
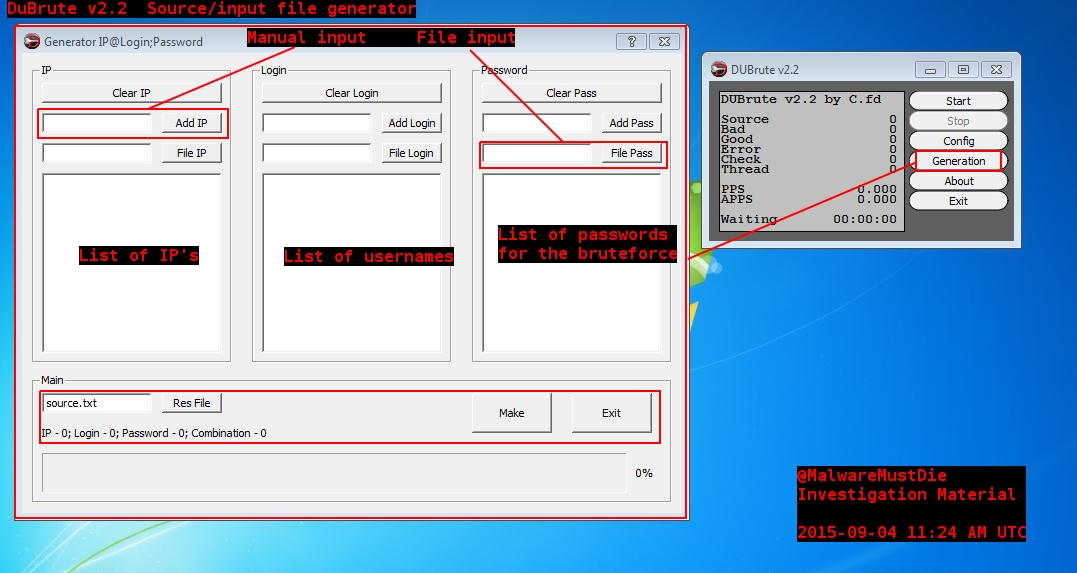
The chinese seem to have problems with this panel. So they made a little tutorial for each other:
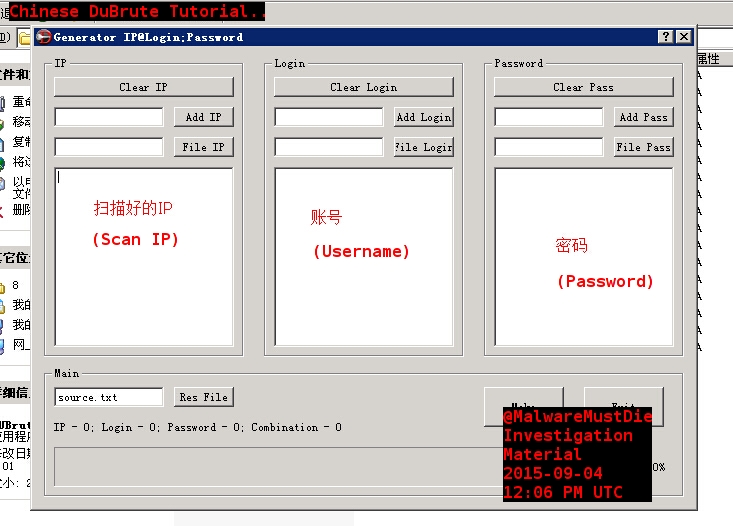
This is the picture that I have found in the panel. I translated the chinese and marked it as Investigation Material. The other .dll’s seems to be dependencies for the bruteforce-tool except one:
The dependencies for dubrute.exe:
cdbdef73515997355e81a99421c1d721 libeay32.dll
86f1895ae8c5e8b17d99ece768a70732 msvcr71.dll
6c06fb9e1d818fde8d142ee180a65646 ssleay32.dll
abf1f45b4fa467b830f091cf96d82586 QtCore4.dll
21e38b4a1f28bdef99d1c7dac5dce164 QtGui4.dllIf you want to examine your system for this kind of hacking-tool feel free to use my yara-rule for it:
rule dubrute : bruteforcer
{
meta:
author = "Christian Rebischke (@sh1bumi)"
date = "2015-09-05"
description = "Rules for DuBrute Bruteforcer"
in_the_wild = true
family = "Hackingtool/Bruteforcer"
strings:
$a = "WBrute"
$b = "error.txt"
$c = "good.txt"
$d = "source.txt"
$e = "bad.txt"
$f = "Generator IP@Login;Password"
condition:
//check for MZ Signature at offset 0
uint16(0) == 0x5A4D
and
//check for dubrute specific strings
$a and $b and $c and $d and $e and $f
}Who else is using DuBrute?
DuBrute is one of the mostly used bruteforcer for windows in the internet. Here are just a few examples who else is using DuBrute:
Russian Carders
Maroccoean Hackercrew
Albanian Hackercrew
some skiddies
AnonSquad
Black Team
Cyberguerilla
and much more..
Let us go to the next binary. This is xiaofe.dll. I analyzed it via PeStudio (thx to Marc Ochsenmeier for this awesome tool).
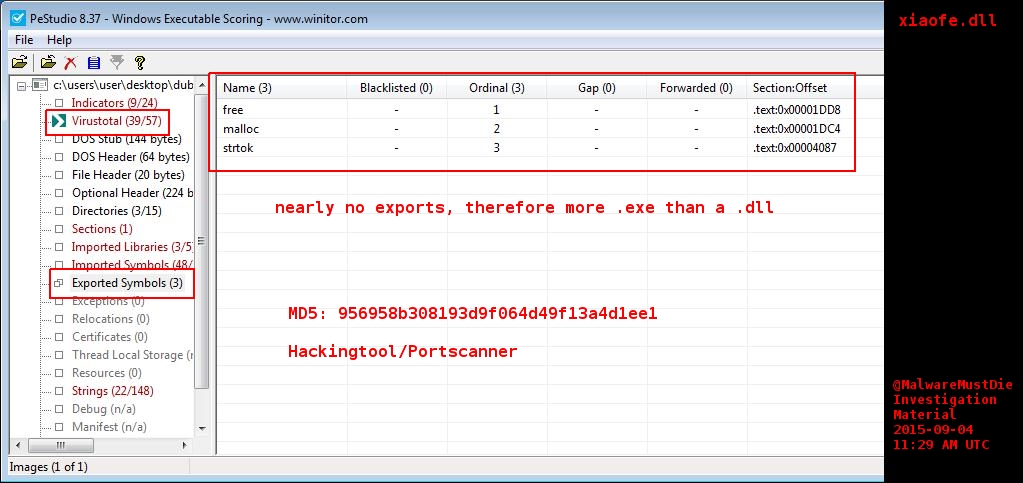
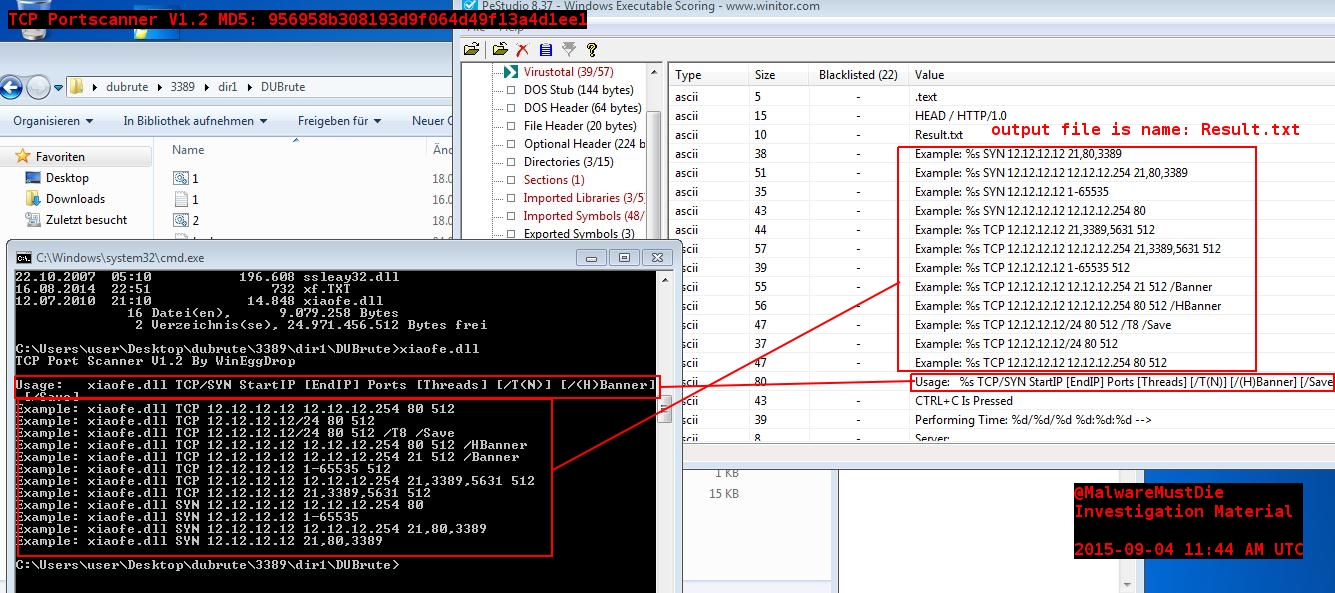
It’s pretty clear a portscanner. I think this doesn’t need more explaination. Here is a yara-rule for this tool, too:
rule wineggdrop : portscanner
{
meta:
author = "Christian Rebischke (@sh1bumi)"
date = "2015-09-05"
description = "Rules for TCP Portscanner VX.X by WinEggDrop"
in_the_wild = true
family = "Hackingtool/Portscanner"
strings:
$a = { 54 43 50 20 50 6f 72 74 20 53 63 61 6e 6e 65 72
20 56 3? 2e 3? 20 42 79 20 57 69 6e 45 67 67 44
72 6f 70 0a }
$b = "Result.txt"
$c = "Usage: %s TCP/SYN StartIP [EndIP] Ports [Threads] [/T(N)] [/(H)Banner] [/Save]\n"
condition:
//check for MZ Signature at offset 0
uint16(0) == 0x5A4D
and
//check for wineggdrop specific strings
$a and $b and $c
}After I analyzed the binaries I went further to the batch files. I didn’t expect something special, but I was nicely surprised:
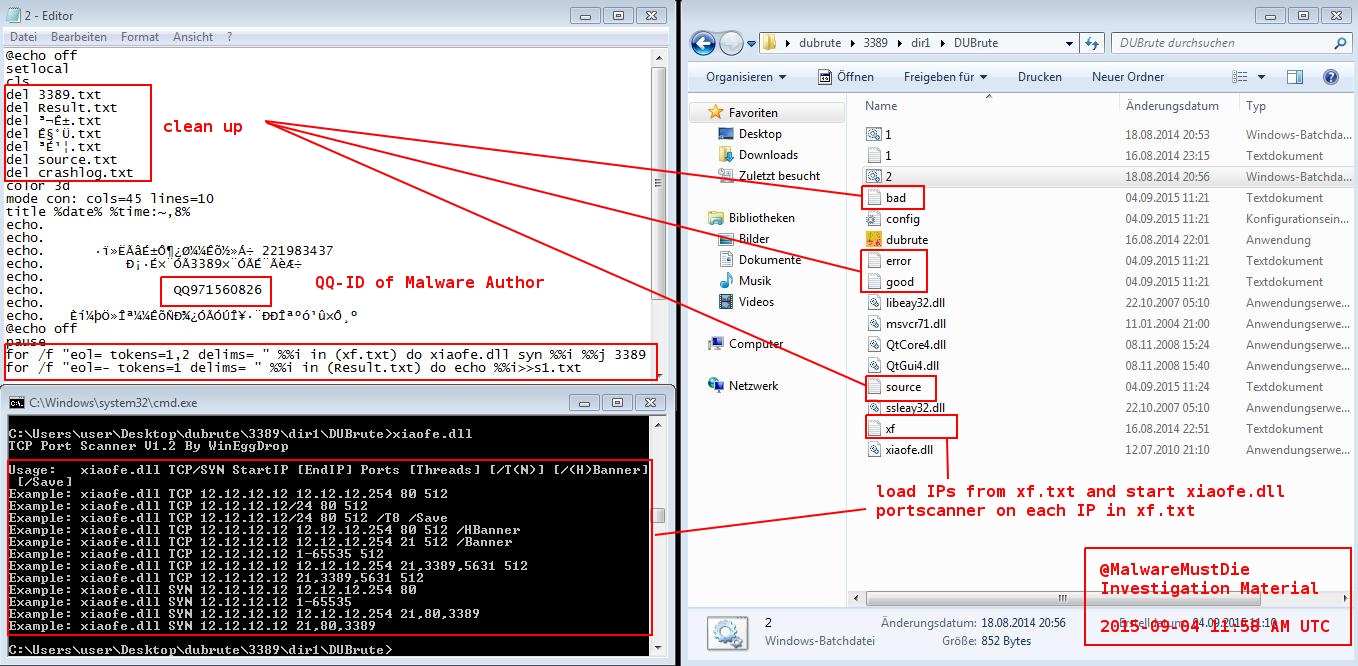
2.bat seems to be a clean-up script. It cleans up the working directory outputs a chinese header (that I can’t read due to encoding problems. When you have an idea how to fix this feel free to email me) and initiates the portscan on all IP’s in the xf.txt file. The interesting part is the QQ ID. (QQ is a famous chinese messenger and mailhoster). This QQ ID leads us to an old known suspect, who is pretty famous for the Linux/Xor.DDoS story:
Here are the virustotal-links to the two binaries:
thanks to my fellow team mates and our supporters for the great assistance.